Whereas chiplets have been round for many years, their use was traditionally restricted to particular, specialised functions. Right this moment, nevertheless, they’re on the forefront of expertise, powering hundreds of thousands of desktop PCs, workstations, servers, gaming consoles, telephones, and even wearable gadgets worldwide.
In a matter of some years, most main chipmakers have embraced chiplet expertise to drive innovation. It is now clear that chiplets are poised to change into the business customary. Let’s discover what makes them so important and the way they’re shaping the way forward for expertise.
TL;DR: What are chiplets?
Chiplets are segmented processors. As a substitute of consolidating each half right into a single chip (often called a monolithic strategy), particular sections are manufactured as separate chips. These particular person chips are then mounted collectively right into a single package deal utilizing a fancy connection system.
This association permits the elements that may profit from the most recent fabrication strategies to be shrunk in dimension, bettering the effectivity of the method and permitting them to slot in extra parts.
The elements of the chip that may’t be considerably diminished or do not require discount could be produced utilizing older and extra economical strategies.
Whereas the method of producing such processors is complicated, the general price is often decrease. Moreover, it provides processor firms a extra manageable pathway to broaden their product vary.
Silicon science
To completely perceive why processor producers have turned to chiplets, we should first delve into how these gadgets are made. CPUs and GPUs begin their life as massive discs fabricated from ultra-pure silicon, usually a bit of beneath 12 inches (300 mm) in diameter and 0.04 inches (1 mm) thick.
This silicon wafer undergoes a sequence of intricate steps, leading to a number of layers of various supplies – insulators, dielectrics, and metals. These layers’ patterns are created by way of a course of known as photolithography, the place ultraviolet gentle is shone by way of an enlarged model of the sample (a masks), and subsequently shrunk through lenses to the required dimension.
The sample will get repeated, at set intervals, throughout the floor of the wafer and every of those will finally change into a processor. Since chips are rectangular and wafers are round, the patterns should overlap the disc’s perimeter. These overlapping elements are finally discarded as they’re non-functional.
As soon as accomplished, the wafer is examined utilizing a probe utilized to every chip. {The electrical} examination outcomes inform engineers in regards to the processor’s high quality towards a protracted listing of standards. This preliminary stage, often called chip binning, helps decide the processor’s “grade.”
For example, if the chip is meant to be a CPU, each half ought to perform accurately, working inside a set vary of clock speeds at a selected voltage. Every wafer part is then categorized primarily based on these take a look at outcomes.
Upon completion, the wafer is reduce into particular person items, or “dies,” which can be viable to be used. These dies are then mounted onto a substrate, akin to a specialised motherboard. The processor undergoes additional packaging (as an illustration, with a warmth spreader) earlier than it is prepared for distribution.
All the sequence can take weeks of producing and corporations resembling TSMC and Samsung cost excessive charges for every wafer, wherever between $3,000 and $20,000 relying on the method node getting used.
“Course of node” is the time period used to explain all the fabrication system. Traditionally, they had been named after the transistor’s gate size. Nevertheless, as manufacturing expertise improved and allowed for ever-smaller parts, the nomenclature not adopted any bodily facet of the die and now it is merely a advertising and marketing instrument.
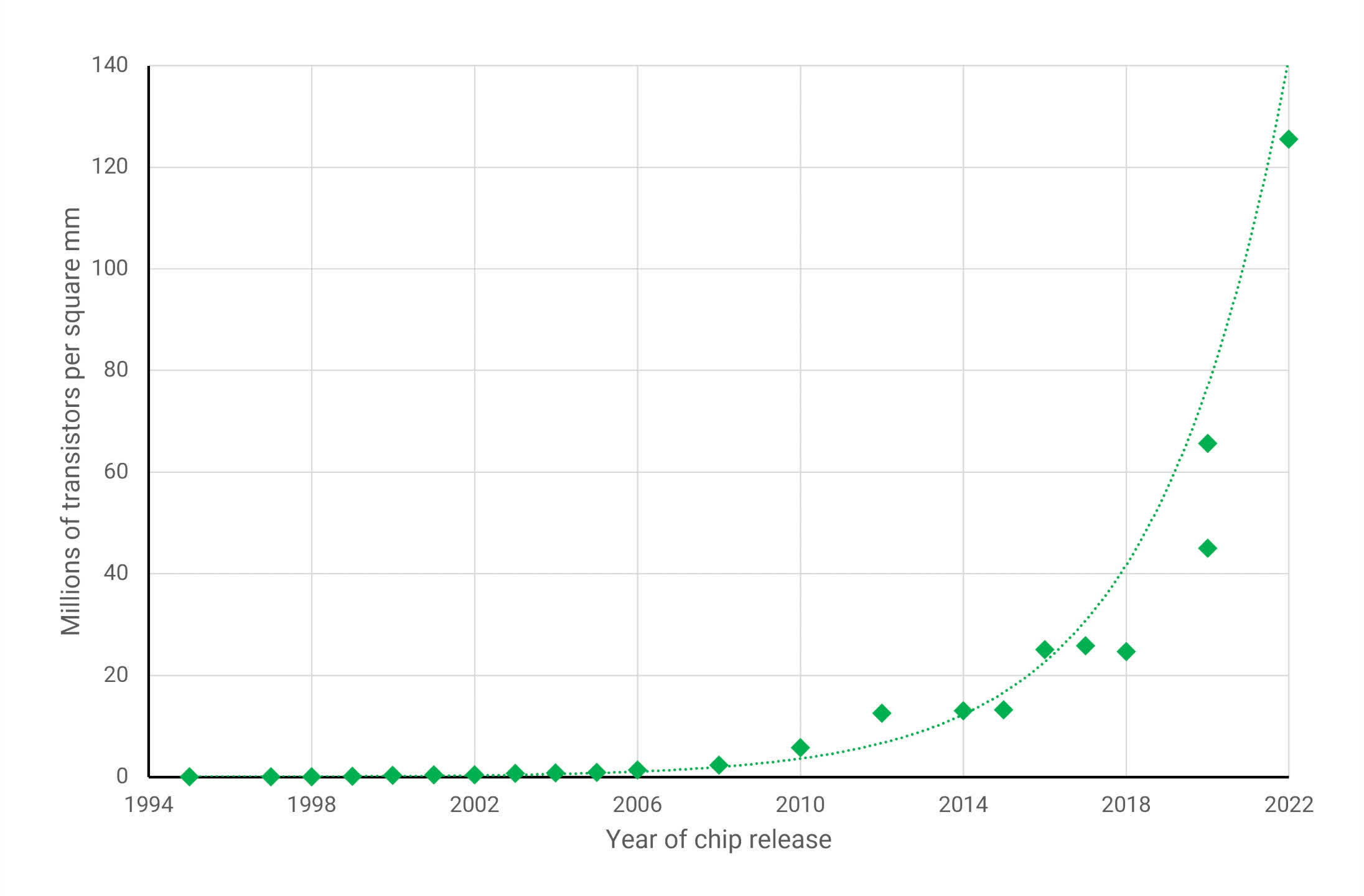
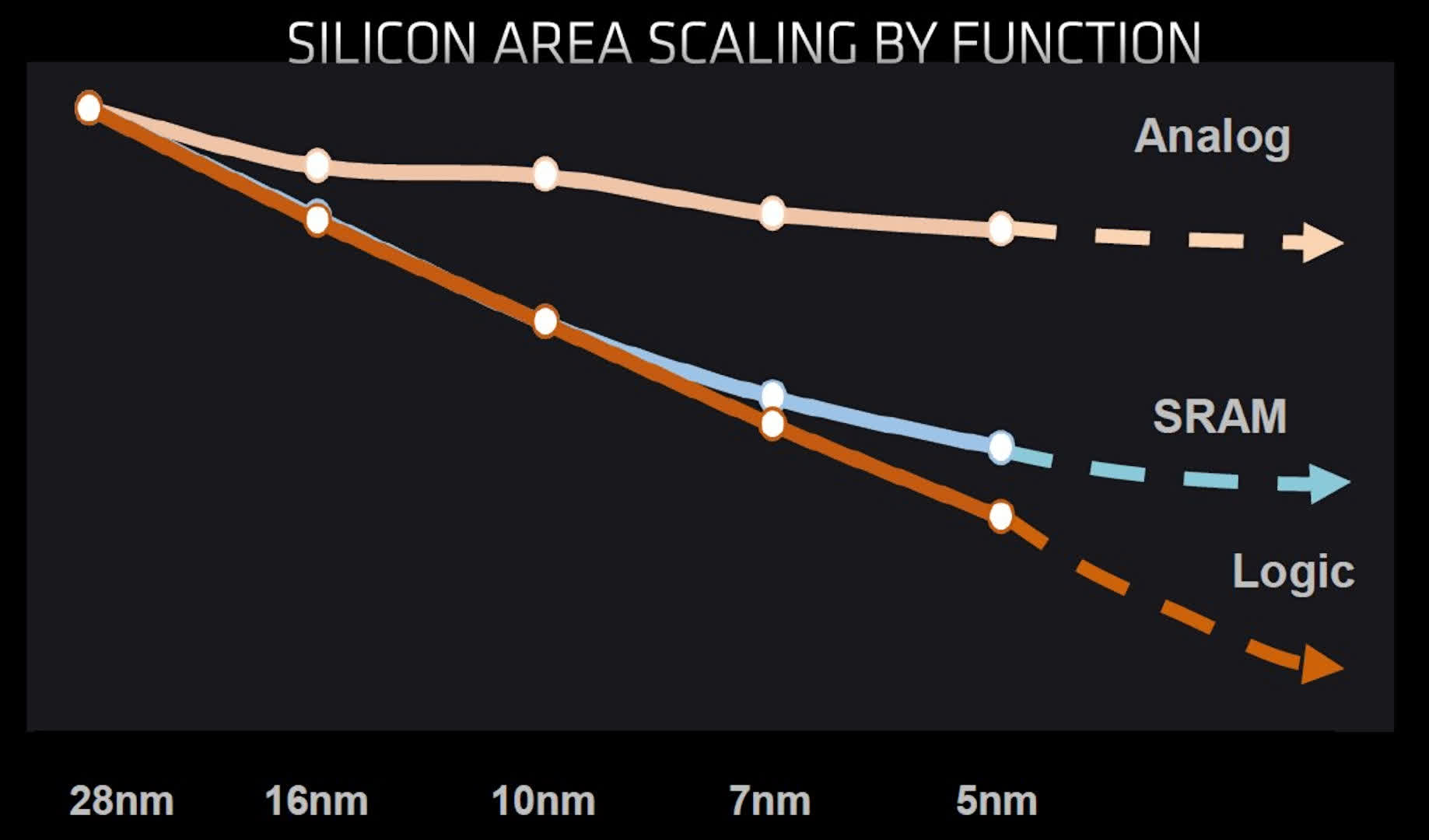
However, every new course of node brings advantages over its predecessor. It could be cheaper to provide, eat much less energy on the identical clock pace (or vice versa), or have the next density. The latter metric measures what number of parts can match inside a given die space. Within the graph under, you’ll be able to see how this has advanced through the years for GPUs (the most important and most complicated chips you will discover in a PC)…
The enhancements in course of nodes present a method for engineers to extend the capabilities and efficiency of their merchandise, with out having to make use of large and expensive chips. Nevertheless, the above graph solely tells a part of the story, as not each facet of a processor can profit from these developments.
Circuits inside chips could be allotted into one of many following broad classes:
- Logic – handles information, math, and decision-making
- Reminiscence – normally SRAM, which shops information for the logic
- Analog – circuits that handle indicators between the chip and different gadgets
Sadly, whereas logic circuits proceed to shrink with each main step ahead in course of node expertise, analog circuits have barely modified and SRAM is beginning to attain a restrict too.
Whereas logic nonetheless kinds the most important portion of the die, the quantity of SRAM in as we speak’s CPUs and GPUs has considerably grown in recent times. For instance, AMD’s Vega 20 chip utilized in its Radeon VII graphics card (2019), featured a mixed whole of 5 MB of L1 and L2 cache. Simply two GPU generations later, the Navi 21 chip powering the Radeon RX 6000 sequence (2020), included over 130 MB of mixed cache – a outstanding 25-fold improve.
We are able to anticipate these to proceed to extend as new generations of processors are developed, however with reminiscence not cutting down in addition to the logic, it’s going to change into more and more much less cost-effective to fabricate the entire circuitry on the identical course of node.
In an excellent world, one would design a die the place analog sections are fabricated on the most important and least expensive node, SRAM elements on a a lot smaller one, and logic reserved for absolutely the cutting-edge expertise. Sadly, this isn’t virtually achievable. Nevertheless, there exists an alternate strategy.
Divide and conquer
In 1995, Intel launched the Pentium II, a successor to its unique P5 processor. What set it aside from different processors on the time was the design hidden beneath its plastic defend: a circuit board housing two chips. The principle chip contained all of the processing logic and analog techniques, whereas one or two separate SRAM modules served as Degree 2 cache.
Whereas Intel manufactured the first chip, the cache was sourced from exterior suppliers. This strategy turned pretty customary for desktop PCs within the mid-to-late Nineties, till advances in semiconductor fabrication allowed logic, reminiscence, and analog techniques to be totally built-in right into a single die.
Whereas Intel continued to dabble with a number of chips in the identical package deal, it largely caught with the so-called monolithic strategy for processors – i.e., one chip for all the pieces. For many processors, there was no want for multiple die, as manufacturing strategies had been proficient (and reasonably priced) sufficient to maintain it easy.
Nevertheless, different firms had been extra eager about following a multi-chip strategy, most notably IBM. In 2004, it was attainable to buy an 8-chip model of the POWER4 server CPU that comprised 4 processors and 4 cache modules, all mounted inside the identical physique (often called a multi-chip module or MCM strategy).
Round this time, the time period “heterogeneous integration” began to seem, partially resulting from analysis work performed by DARPA. Heterogeneous integration goals to separate the assorted sections of a processing system, fabricate them individually on nodes greatest fitted to every, after which mix them into the identical package deal.
Right this moment, that is higher often called system-in-package (SiP) and has been the usual methodology for equipping smartwatches with chips from their inception. For instance, the Collection 1 Apple Watch homes a CPU, some DRAM and NAND Flash, a number of controllers, and different parts inside a single construction.
The same setup could be achieved by having totally different techniques all on a single die (often called an SoC or system-on-a-chip). Nevertheless, this strategy does not permit for benefiting from totally different node costs, nor can each element be manufactured this fashion.
For a expertise vendor, utilizing heterogeneous integration for a distinct segment product is one factor, however using it for almost all of their portfolio is one other. That is precisely what AMD did with its vary of processors. In 2017, the semiconductor large launched its Zen structure with the launch of the single-die Ryzen desktop CPU. Just some months later, AMD debuted two multi-chip product strains: Threadripper and EPYC, with the latter that includes configurations of as much as 4 dies.
With the launch of Zen 2 two years later, AMD totally embraced HI, MCM, SiP – name it what you’ll. They shifted nearly all of the analog techniques out of the processor and positioned them right into a separate die. These had been manufactured on an easier, cheaper course of node, whereas a extra superior one was used for the remaining logic and cache.
And so, chiplets turned the buzzword of alternative.
Smaller is best
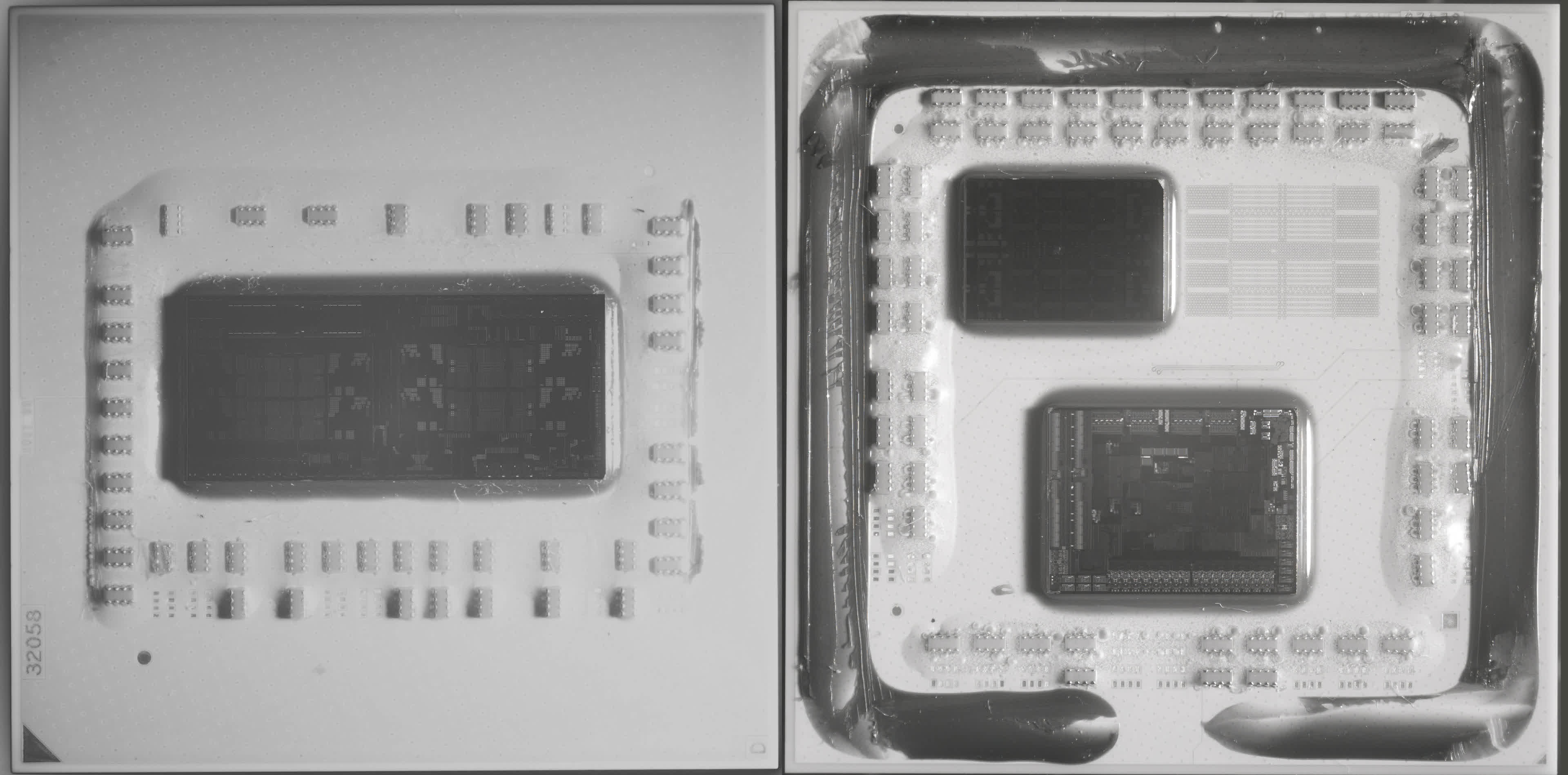
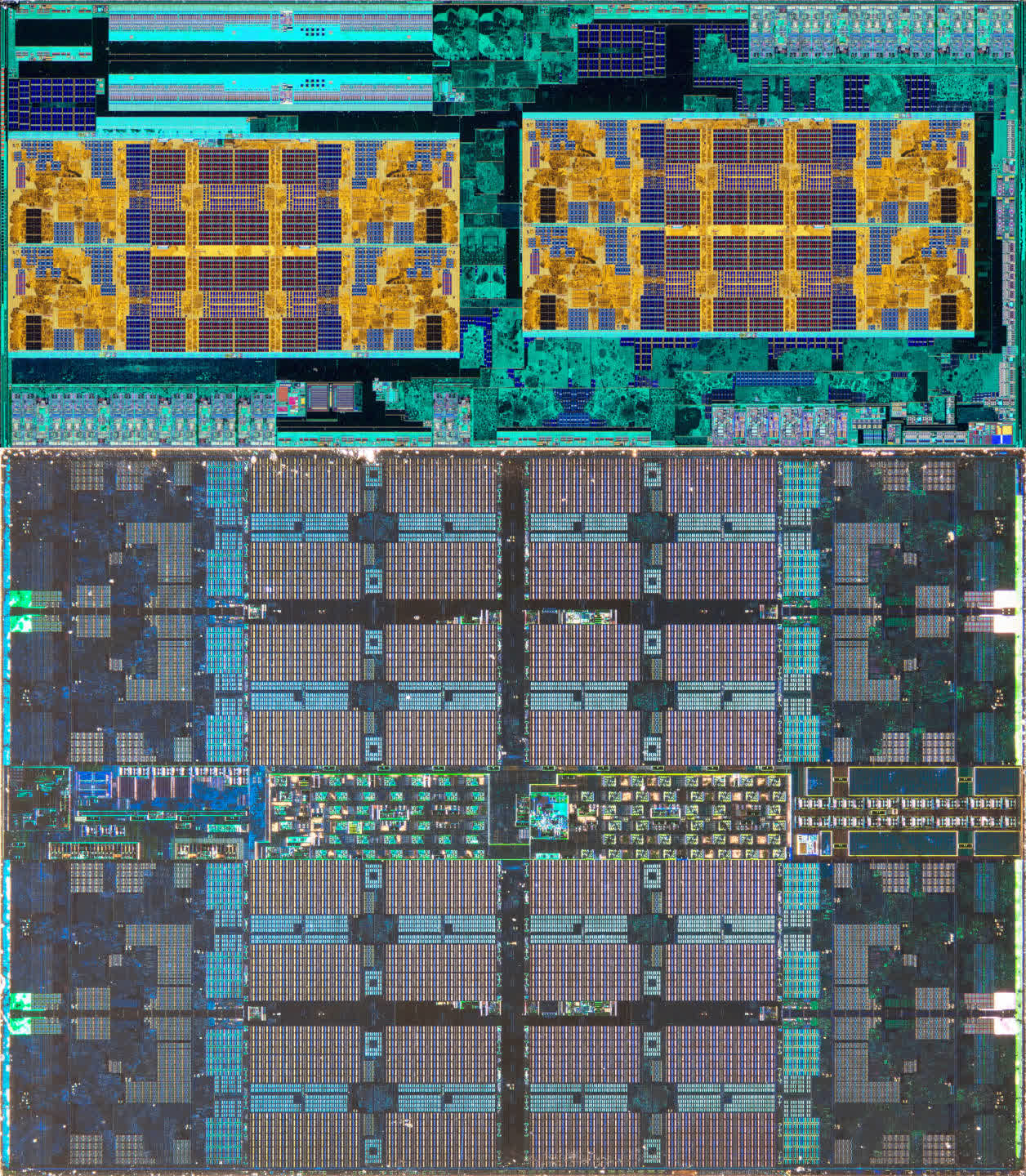
To grasp precisely why AMD selected this course, let’s study the picture under. It showcases two older CPUs from the Ryzen 5 sequence – the 2600 on the left, using the so-called Zen+ structure, and the Zen 2-powered 3600 on the suitable.
The warmth spreaders on each fashions have been eliminated, and the pictures had been taken utilizing an infrared digital camera. The 2600’s single die homes eight cores, although two of them are disabled for this specific mannequin.
That is additionally the case for the 3600, however right here we are able to see that there are two dies within the package deal – the Core Complicated Die (CCD) on the prime, housing the cores and cache, and the Enter/Output Die (IOD) on the backside containing all of the controllers (for reminiscence, PCI Categorical, USB, and so on.) and bodily interfaces.
Since each Ryzen CPUs match into the identical motherboard socket, the 2 photos are basically to scale. On the floor, it might sound that the 2 dies within the 3600 have a bigger mixed space than the one chip within the 2600, however appearances could be deceiving.
If we immediately evaluate the chips containing the cores, it is clear how a lot house within the older mannequin is taken up by analog circuitry – it is all of the blue-green colours surrounding the gold-colored cores and cache. Nevertheless, within the Zen 2 CCD, little or no die space is devoted to analog techniques; it is virtually solely composed of logic and SRAM.
The Zen+ chip has an space of 213 mm² and was manufactured by GlobalFoundries utilizing its 12nm course of node. For Zen 2, AMD retained GlobalFoundries’ providers for the 125 mm² IOD however utilized TSMC’s superior N7 node for the 73 mm² CCD.
The mixed space of the chips within the newer mannequin is smaller, and it additionally boasts twice as a lot L3 cache, supporting sooner reminiscence and PCI Categorical. One of the best a part of the chiplet strategy, nevertheless, was that the compact dimension of the CCD made it attainable for AMD to suit one other one into the package deal. This growth gave beginning to the Ryzen 9 sequence, providing 12 and 16-core fashions for desktop PCs.
Even higher, through the use of two smaller chips as a substitute of 1 massive one, every wafer can probably yield extra dies. Within the case of the Zen 2 CCD, a single 12-inch (300 mm) wafer can produce as much as 85% extra dies than for the Zen+ mannequin.
The smaller the slice one takes out of a wafer, the much less seemingly one goes to search out manufacturing defects (as they are usually randomly distributed throughout the disc), so taking all of this under consideration, the chiplet strategy not solely gave AMD the flexibility to broaden its portfolio, it did so way more cost-effectively – the identical CCDs can be utilized in a number of fashions and every wafer produces lots of of them!
But when this design alternative is so advantageous, why is not Intel doing it? Why aren’t we seeing it being utilized in different processors, like GPUs?
Following the lead
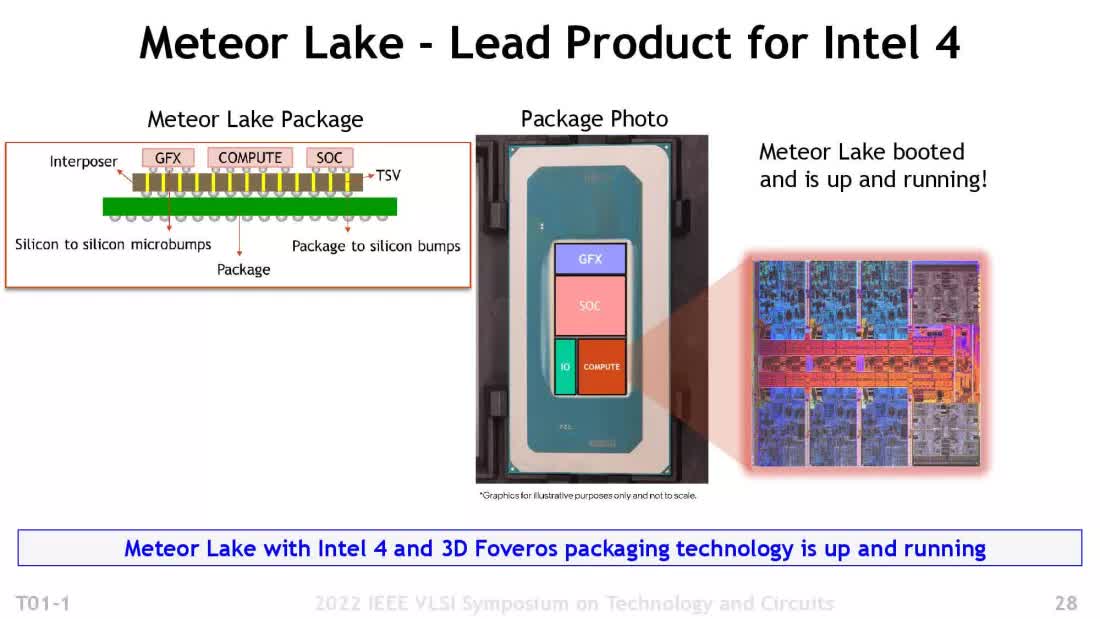
To handle the primary query, Intel has been progressively adopting chiplet expertise as effectively. The primary shopper CPU structure they shipped utilizing chiplets is named Meteor Lake. Intel’s strategy is considerably distinctive although, so let’s discover the way it differs from AMD’s strategy.
Utilizing the time period tiles as a substitute of chiplets, this technology of processors break up the beforehand monolithic design into 4 separate chips:
- Compute tile: Accommodates the entire cores and L2 cache
- GFX tile: Homes the built-in GPU
- SoC tile: Incorporates L3 cache, PCI Categorical, and different controllers
- IO tile: Accommodates the bodily interfaces for reminiscence and different gadgets
Excessive-speed, low-latency connections are current between the SoC and the opposite three tiles, and all of them are linked to a different die, often called an interposer. This interposer delivers energy to every chip and accommodates the traces between them. The interposer and 4 tiles are then mounted onto an extra board to permit the entire meeting to be packaged.
In contrast to Intel, AMD doesn’t use any particular mounting die however has its personal distinctive connection system, often called Infinity Cloth, to deal with chiplet information transactions. Energy supply runs by way of a reasonably customary package deal, and AMD additionally makes use of fewer chiplets. So why is Intel’s design as such?
One problem with AMD’s strategy is that it isn’t very appropriate for the ultra-mobile, low-power sector. For this reason AMD nonetheless makes use of monolithic CPUs for that section. Intel’s design permits them to combine and match totally different tiles to suit a selected want. For instance, funds fashions for reasonably priced laptops can use a lot smaller tiles all over the place, whereas AMD solely has one dimension chiplet for every function.
The draw back to Intel’s system is that it is complicated and costly to provide (which has result in totally different type of points). Each CPU corporations, nevertheless, are totally dedicated to the chiplet idea. As soon as each a part of the manufacturing chain is engineered round it, prices ought to lower.
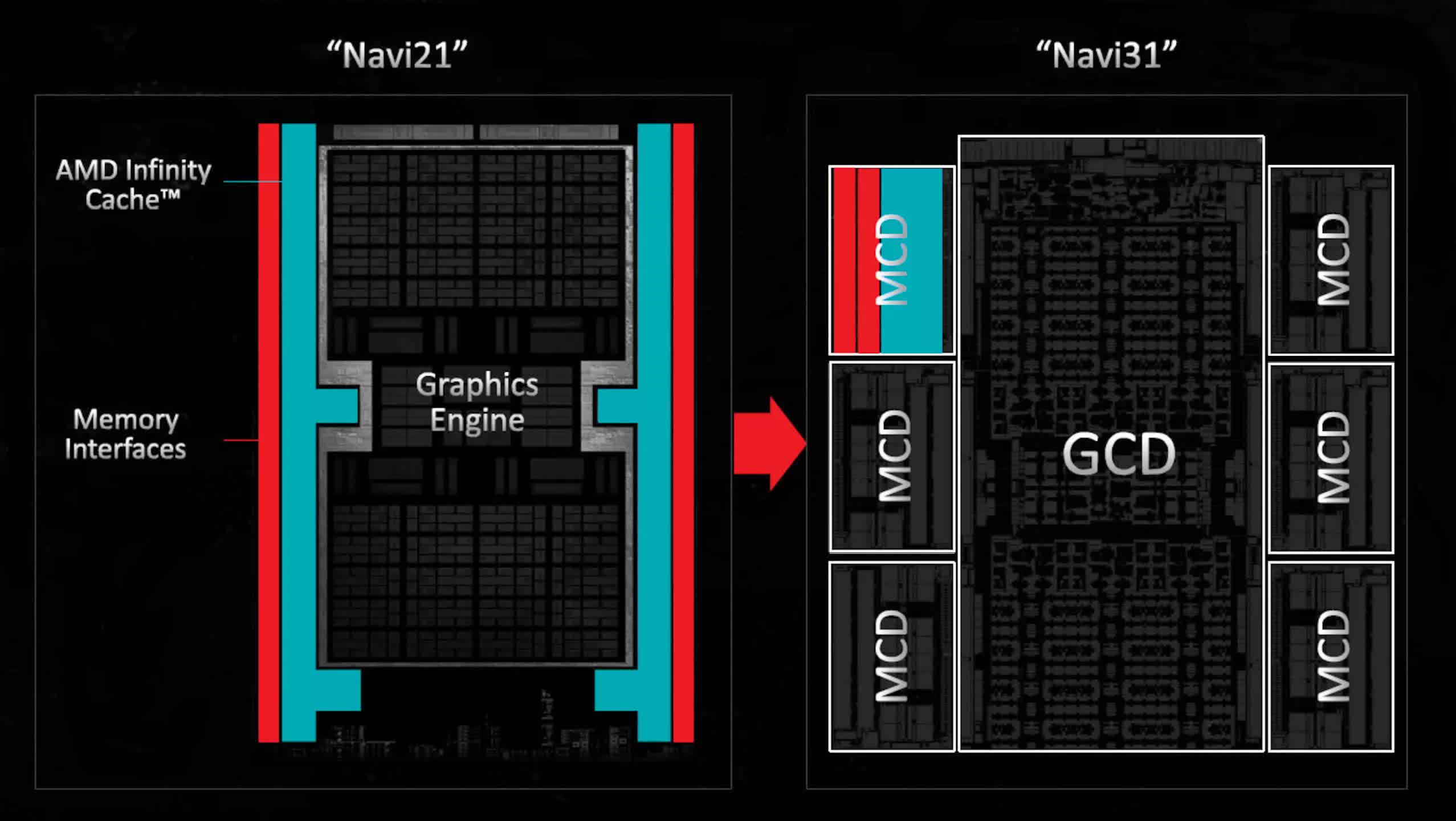
In terms of GPUs, they include comparatively little analog circuitry in comparison with the remainder of the die. Nevertheless, the quantity of SRAM inside has been steadily growing. This pattern prompted AMD to leverage its chiplet experience within the Radeon 7000 sequence, with the Radeon RX 7900 GPUs that includes a multi-die design. These GPUs embrace a single massive die for the cores and L2 cache, together with 5 or 6 smaller dies, every containing a slice of L3 cache and a reminiscence controller.
By transferring these parts out of the principle die, engineers had been capable of considerably improve the quantity of logic with out counting on the most recent, most costly course of nodes to maintain chip sizes manageable. Whereas this innovation seemingly helped cut back total prices, it didn’t considerably broaden the breadth of AMD’s graphics portfolio.
At present, Nvidia and Intel shopper GPUs are exhibiting no indicators of adopting AMD’s chiplet strategy. Each firms depend on TSMC for all manufacturing duties and appear content material to provide extraordinarily massive chips, passing the price onto shoppers.
That mentioned, it’s identified that each are actively exploring and implementing chiplet-based architectures in a few of their GPU designs. For instance, Nvidia’s Blackwell information middle GPUs make the most of a chiplet design that includes two massive dies linked through a high-speed interlink able to 10 terabytes per second, successfully functioning as a single GPU.
Getting Moore with chiplets
Irrespective of when these modifications happen, the basic fact is that they should occur. Regardless of the large technological advances in semiconductor manufacturing, there’s a particular restrict to how a lot every element could be shrunk.
To proceed enhancing chip efficiency, engineers basically have two avenues – add extra logic, with the mandatory reminiscence to assist it, and improve inner clock speeds. Concerning the latter, the common CPU hasn’t considerably altered on this facet for years. AMD’s FX-9590 processor, from 2013, might attain 5 GHz in sure workloads, whereas the best clock pace in its present fashions is 5.7 GHz (with the Ryzen 9 9950X).
Intel’s highest-clocked shopper CPU is the Core i9-14900KS, that includes a most turbo frequency of 6.2 GHz on two cores. This “particular version” processor holds the file for the quickest out-of-the-box clock pace amongst desktop CPUs.
Nevertheless, what has modified is the quantity of circuitry and SRAM. The aforementioned AMD FX-9590 had 8 cores (and eight threads) and eight MB of L3 cache, whereas the 9950X boasts 16 cores, 32 threads, and 64 MB of L3 cache. Intel’s CPUs have equally expanded by way of cores and SRAM.
Nvidia’s first unified shader GPU, the G80 from 2006, consisted of 681 million transistors, 128 cores, and 96 kB of L2 cache in a chip measuring 484 mm2 in space. Quick ahead to 2022, when the AD102 was launched, and it now contains 76.3 billion transistors, 18,432 cores, and 98,304 kB of L2 cache inside 608 mm2 of die space.
In 1965, Fairchild Semiconductor co-founder Gordon Moore noticed that within the early years of chip manufacturing, the density of parts inside a die was doubling every year for a set minimal manufacturing price. This statement turned often called Moore’s Regulation and was later interpreted to imply “the variety of transistors in a chip doubles each two years”, primarily based on manufacturing tendencies.
Moore’s Regulation has served as a fairly correct illustration of the semiconductor business’s progress for practically six many years. The large good points in logic and reminiscence in each CPUs and GPUs have largely been pushed by steady enhancements in course of nodes, with parts changing into progressively smaller over time. Nevertheless, this pattern can not cannot proceed ceaselessly, no matter what new expertise comes about.
Quite than ready for these bodily limits to be reached, firms like AMD and Intel have embraced chiplet expertise, exploring progressive methods to mix these modular parts to maintain the creation of more and more highly effective processors.
A long time sooner or later, the common PC could be residence to CPUs and GPUs the dimensions of your hand. However, peel off the warmth spreader and you will find a number of tiny chips – not three or 4, however dozens of them, all ingeniously tiled and stacked collectively. The dominance of the chiplet has solely simply begun.