Nvidia could also be becoming a member of AMD and Intel in growing a multi-chiplet structure for its subsequent technology of GPUs, and will reap main positive factors by way of efficiency.
Nvidia is the final of the large three chipmakers that also makes use of a single slice of silicon for the processors inside its finest graphics playing cards, so it is one thing of a welcome shock that rumors have begun circulating that the corporate will lastly transfer to the extra adaptable multi-chiplet module (MCM) design with its next-generation Nvidia Blackwell structure.
The report comes from well-known {hardware} leaker @kopite7kimi on X, who mentioned that Nvidia’s commercial-grade GB100 GPU will function MCM for the primary time.
After the dramas of GA100 and GH100, plainly GB100 is lastly going to make use of MCM.September 18, 2023
The Nvidia Blackwell structure is predicted to energy each Nvidia’s next-gen industrial GPU merchandise, that are utilized by information facilities and industial-scale customers, in addition to its client graphics playing cards, the Nvidia RTX 5000 collection.
Despite the fact that each will use the Blackwell structure, nevertheless, it is unclear for the time being if the MCM shift can even prolong to the Nvidia 5000 collection graphics playing cards. If it does, although, it may present the transformational efficiency for Nvidia’s subsequent graphics card technology that was usually missing in a few of its more moderen RTX 4000-series playing cards.
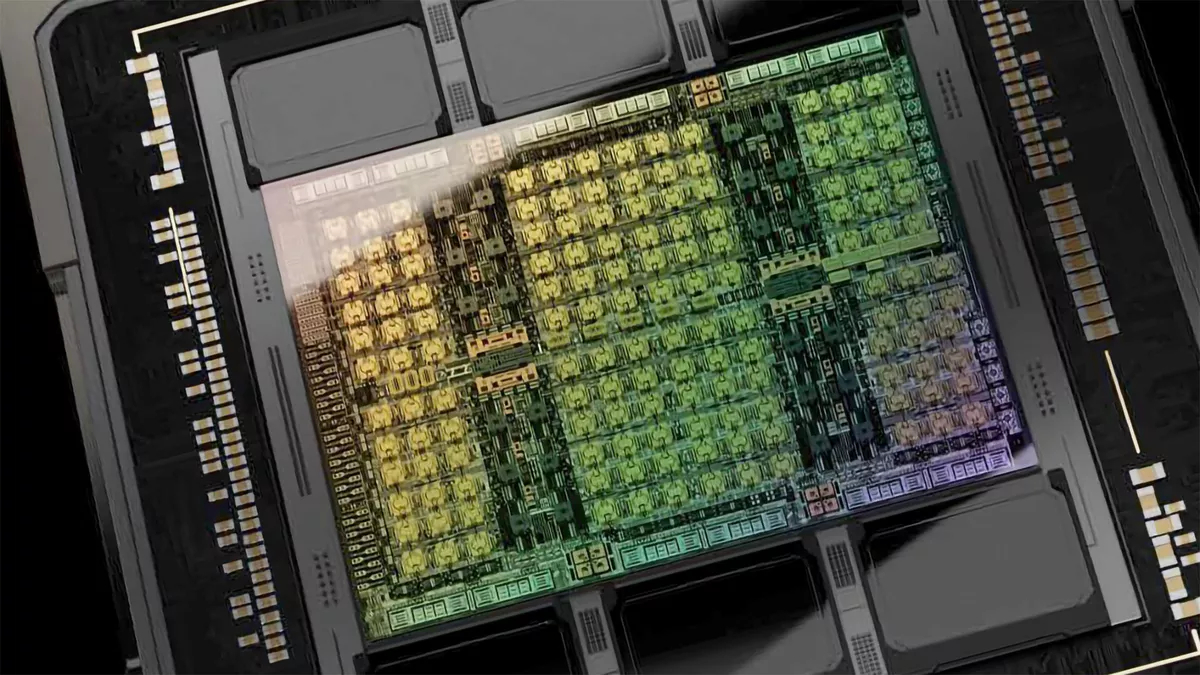
The chiplets in an MCM design, when interconnected right into a single processor, guarantees considerably quicker efficiency over a monolithic slab of silicon. As Tom’s {Hardware} explains, a single silicon chip is constrained by the bodily dimensions of the gear used to manufacture it. Presently, the method Nvidia makes use of can solely produce a 26mm by 33mm (858mm²) items of silicon at most, and Nvidia’s commercial-grade GPUs are already bumping proper up in opposition to that most dimension.
And because it’s turn into exponentially harder to additional shrink the scale of a transistor, the digital change inside a chip that produces a pc’s logic performance, the one option to enhance the variety of transistors in your GPU to extend efficiency is to make the chip bigger than the bodily manufacturing course of will enable.
That is the place the chiplets are available. When you can produce two or extra chiplets which might be smaller, however use particular ties referred to as interconnects to hyperlink them collectively so that they act as a single unit, you may successfully construct a bigger chip than the fabrication course of can supprt and dramatically enhance efficiency. With an MCM design for its GPUs, Nvidia would possibly have the ability to ship the sorts of positive factors throughout its complete portfolio of Nvidia 5000 collection playing cards that many have been hoping to see with the 4000 collection however which Nvidia wasn’t capable of ship persistently.
Clearly, that is nonetheless very speculative and based mostly on rumors, however there is a cause why each AMD and Intel have made the change to MCM of their GPUs and CPUs, and Nvidia could be very good to comply with swimsuit, or danger getting left behind.
Make the transfer to MCM, Nvidia, it is the one means ahead
The issue chip makers have been having for years now has been the top of Moore’s Regulation, the well-known prediction by Intel co-founder Gordon Moore that transistor density on a chip would double roughly each two years.
For 50 years, that had been the case, however as we now measure the scale of transistors relative to the diameter of particular person atoms within the silicon, chopping a transistor’s dimension in half simply is not attainable anymore.
However customers and business have turn into used to quicker computer systems each couple of years, and so nobody actually needs to listen to that the social gathering is over. When you’re a chip maker seeking to preserve promoting extra processors, it’s important to discover one other option to ship these efficiency positive factors the market expects, Moore’s Regulation be damned.
The reply to that is utilizing a number of chips together with each other to attain these efficiency targets. We have already been doing this for greater than a decade, as Nvidia nicely is aware of.
There was a time when there was no such factor as a graphics processor, there was simply the primary CPU which was anticipated to deal with graphics in addition to each different operation.
As graphics grew to become extra superior although, this so closely taxed the CPU that one thing needed to be executed earlier than computing 3D scenes both ate up 99.9% of the CPU’s clock cycles, or the bounds of the CPU itself floor pc graphics progress to a halt.
The work round was to go all however probably the most primary graphics processing work off to a second processor, the GPU, which was specifically designed for this process and which went on to energy the fashionable period of pc graphics. Nvidia is aware of this as a result of it was the one which created the world’s first GPU, the Nvidia GeForce 256, again in 1999.
We have come full circle then, and graphics processors are so overwhelmed with the workloads being assigned to them that they can not sustain and we won’t squeeze extra efficiency out of the same-sized silicon. It is time then to interrupt up geometry, rasterization, ray tracing, machine studying, and different GPU workloads into completely different mini-processors that may be particularly engineered to carry out these duties quicker and extra effectively than we’re presently doing.
Nvidia’s chief competitor, AMD, is already doing this and it is seen very constructive outcomes up to now. And whereas the primary few makes an attempt to get MCM engineering proper may not be the revolution that the primary GPU was when it landed over 20 years in the past, future makes an attempt will get us to the place we would like—and Nvidia wants—to be, so Nvidia ought to most likely get to work on that.




