Aurich Lawson | Getty Pictures
On Tuesday, researchers from Google and Tel Aviv College unveiled GameNGen, a brand new AI mannequin that may interactively simulate the basic 1993 first-person shooter recreation Doom in actual time utilizing AI picture era strategies borrowed from Steady Diffusion. It is a neural community system that may perform as a restricted recreation engine, doubtlessly opening new prospects for real-time online game synthesis sooner or later.
For instance, as an alternative of drawing graphical video frames utilizing conventional strategies, future video games might doubtlessly use an AI engine to “think about” or hallucinate graphics in actual time as a prediction job.
“The potential right here is absurd,” wrote app developer Nick Dobos in response to the information. “Why write advanced guidelines for software program by hand when the AI can simply assume each pixel for you?”
GameNGen can reportedly generate new frames of Doom gameplay at over 20 frames per second utilizing a single tensor processing unit (TPU), a kind of specialised processor just like a GPU that’s optimized for machine studying duties.
In checks, the researchers say that ten human raters typically failed to tell apart between quick clips (1.6 seconds and three.2 seconds) of precise Doom recreation footage and outputs generated by GameNGen, figuring out the true gameplay footage 58 % or 60 % of the time.
An instance of GameNGen in motion, interactively simulating Doom utilizing a picture synthesis mannequin.
Actual-time online game synthesis utilizing what is likely to be referred to as “neural rendering” shouldn’t be a very novel thought. Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang predicted throughout an interview in March, maybe considerably boldly, that almost all online game graphics could possibly be generated by AI in actual time inside 5 to 10 years.
GameNGen additionally builds on earlier work within the area, cited within the GameNGen paper, that features World Fashions in 2018, GameGAN in 2020, and Google’s personal Genie in March. And a gaggle of college researchers educated an AI mannequin (referred to as “DIAMOND“) to simulate classic Atari video video games utilizing a diffusion mannequin earlier this 12 months.
Additionally, ongoing analysis into “world fashions” or “world simulators,” generally related to AI video synthesis fashions like Runway’s Gen-3 Alpha and OpenAI’s Sora, is leaning towards an analogous path. For instance, through the debut of Sora, OpenAI confirmed demo movies of the AI generator simulating Minecraft.
Diffusion is vital
In a preprint analysis paper titled “Diffusion Fashions Are Actual-Time Recreation Engines,” authors Dani Valevski, Yaniv Leviathan, Moab Arar, and Shlomi Fruchter clarify how GameNGen works. Their system makes use of a modified model of Steady Diffusion 1.4, a picture synthesis diffusion mannequin launched in 2022 that individuals use to supply AI-generated photos.
“Seems the reply to ‘can it run DOOM?’ is sure for diffusion fashions,” wrote Stability AI Analysis Director Tanishq Mathew Abraham, who was not concerned with the analysis undertaking.
Whereas being directed by participant enter, the diffusion mannequin predicts the subsequent gaming state from earlier ones after having been educated on in depth footage of Doom in motion.
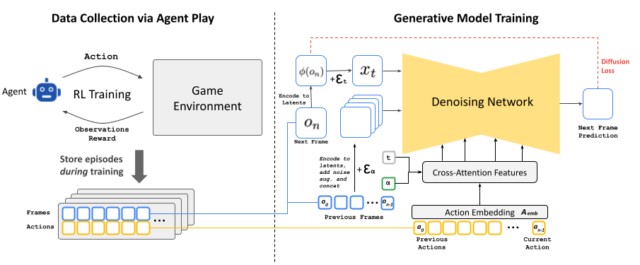
The event of GameNGen concerned a two-phase coaching course of. Initially, the researchers educated a reinforcement studying agent to play Doom, with its gameplay classes recorded to create an robotically generated coaching dataset—that footage we talked about. They then used that knowledge to coach the customized Steady Diffusion mannequin.
Nevertheless, utilizing Steady Diffusion introduces some graphical glitches, because the researchers observe of their summary: “The pre-trained auto-encoder of Steady Diffusion v1.4, which compresses 8×8 pixel patches into 4 latent channels, ends in significant artifacts when predicting recreation frames, which have an effect on small particulars and notably the underside bar HUD.”
An instance of GameNGen in motion, interactively simulating Doom utilizing a picture synthesis mannequin.
And that is not the one problem. Conserving the photographs visually clear and constant over time (usually referred to as “temporal coherency” within the AI video house) could be a problem. GameNGen researchers say that “interactive world simulation is extra than simply very quick video era,” as they write of their paper. “The requirement to situation on a stream of enter actions that’s solely accessible all through the era breaks some assumptions of current diffusion mannequin architectures,” together with repeatedly producing new frames based mostly on earlier ones (referred to as “autoregression”), which may result in instability and a fast decline within the high quality of the generated world over time.

Aurich Lawson | Getty Pictures
On Tuesday, researchers from Google and Tel Aviv College unveiled GameNGen, a brand new AI mannequin that may interactively simulate the basic 1993 first-person shooter recreation Doom in actual time utilizing AI picture era strategies borrowed from Steady Diffusion. It is a neural community system that may perform as a restricted recreation engine, doubtlessly opening new prospects for real-time online game synthesis sooner or later.
For instance, as an alternative of drawing graphical video frames utilizing conventional strategies, future video games might doubtlessly use an AI engine to “think about” or hallucinate graphics in actual time as a prediction job.
“The potential right here is absurd,” wrote app developer Nick Dobos in response to the information. “Why write advanced guidelines for software program by hand when the AI can simply assume each pixel for you?”
GameNGen can reportedly generate new frames of Doom gameplay at over 20 frames per second utilizing a single tensor processing unit (TPU), a kind of specialised processor just like a GPU that’s optimized for machine studying duties.
In checks, the researchers say that ten human raters typically failed to tell apart between quick clips (1.6 seconds and three.2 seconds) of precise Doom recreation footage and outputs generated by GameNGen, figuring out the true gameplay footage 58 % or 60 % of the time.
An instance of GameNGen in motion, interactively simulating Doom utilizing a picture synthesis mannequin.
Actual-time online game synthesis utilizing what is likely to be referred to as “neural rendering” shouldn’t be a very novel thought. Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang predicted throughout an interview in March, maybe considerably boldly, that almost all online game graphics could possibly be generated by AI in actual time inside 5 to 10 years.
GameNGen additionally builds on earlier work within the area, cited within the GameNGen paper, that features World Fashions in 2018, GameGAN in 2020, and Google’s personal Genie in March. And a gaggle of college researchers educated an AI mannequin (referred to as “DIAMOND“) to simulate classic Atari video video games utilizing a diffusion mannequin earlier this 12 months.
Additionally, ongoing analysis into “world fashions” or “world simulators,” generally related to AI video synthesis fashions like Runway’s Gen-3 Alpha and OpenAI’s Sora, is leaning towards an analogous path. For instance, through the debut of Sora, OpenAI confirmed demo movies of the AI generator simulating Minecraft.
Diffusion is vital
In a preprint analysis paper titled “Diffusion Fashions Are Actual-Time Recreation Engines,” authors Dani Valevski, Yaniv Leviathan, Moab Arar, and Shlomi Fruchter clarify how GameNGen works. Their system makes use of a modified model of Steady Diffusion 1.4, a picture synthesis diffusion mannequin launched in 2022 that individuals use to supply AI-generated photos.
“Seems the reply to ‘can it run DOOM?’ is sure for diffusion fashions,” wrote Stability AI Analysis Director Tanishq Mathew Abraham, who was not concerned with the analysis undertaking.

Whereas being directed by participant enter, the diffusion mannequin predicts the subsequent gaming state from earlier ones after having been educated on in depth footage of Doom in motion.
The event of GameNGen concerned a two-phase coaching course of. Initially, the researchers educated a reinforcement studying agent to play Doom, with its gameplay classes recorded to create an robotically generated coaching dataset—that footage we talked about. They then used that knowledge to coach the customized Steady Diffusion mannequin.
Nevertheless, utilizing Steady Diffusion introduces some graphical glitches, because the researchers observe of their summary: “The pre-trained auto-encoder of Steady Diffusion v1.4, which compresses 8×8 pixel patches into 4 latent channels, ends in significant artifacts when predicting recreation frames, which have an effect on small particulars and notably the underside bar HUD.”
An instance of GameNGen in motion, interactively simulating Doom utilizing a picture synthesis mannequin.
And that is not the one problem. Conserving the photographs visually clear and constant over time (usually referred to as “temporal coherency” within the AI video house) could be a problem. GameNGen researchers say that “interactive world simulation is extra than simply very quick video era,” as they write of their paper. “The requirement to situation on a stream of enter actions that’s solely accessible all through the era breaks some assumptions of current diffusion mannequin architectures,” together with repeatedly producing new frames based mostly on earlier ones (referred to as “autoregression”), which may result in instability and a fast decline within the high quality of the generated world over time.






