After I first heard
Samsung
speak up AI upscaling in its 8K TVs, I assumed it was the age-old advertising observe of smashing a new buzzword onto some previous tech and proclaiming it super-fancy.
Which may not be the case. Whereas including Synthetic Intelligence is not going to instantly make your TV smarter, or sentient (but), there are theoretical advantages to AI-enhanced video. How a lot precise enchancment stays to be seen — we’ve not thus far reviewed any TVs with this characteristic. However the prospects are intriguing.
Tech corporations make use of synthetic intelligence in varied methods — from facial recognition to digital assistants like Alexa and Siri to serving to advance training and drugs. Utilizing it to enhance picture high quality — particularly the mandatory conversion from decrease decision video frequent as we speak to greater 4K and 8K resolutions on TV screens — is one thing new, and an enormous focus for Samsung. The corporate is together with AI upscaling in its 8K and 4K QLED TVs this yr.
One large cause to care about upscaling know-how is as a result of high-resolution video, particularly 8K, continues to be a number of years away. We do not even have widespread 4K TV broadcasts but within the US. Till they develop into extra frequent, you will nonetheless be watching numerous 1080p and decrease decision sources in your shiny, new 4K or 8K TV. Improved upscaling could make these sources look higher, particularly on bigger screens.

Watch this: Samsung Q900 85-inch 8K TV hands-on: A stupendous beast
Chief Samsung TV rival
LG
is doubling down on “AI” too. It is utilizing the time period in 2019 TVs for comfort options like Google Assistant and
sensible dwelling
integration, in addition to for image-quality enhancements.
Sony
, however, would not name its image processing “AI,” but it capabilities in a considerably comparable method to Samsung’s AI upscaling.
So how does Samsung’s know-how work, and why is it extra intriguing than commonplace marketing-speak? Let’s begin firstly.
What’s scaling?
All fashionable televisions have a set variety of pixels, or particular person image parts — tiny blocks that mix collectively to create the image. That is their decision, and is often known as 1080p, Extremely HD 4K, or now 8K. Your present TV, if it is a number of years previous, is probably going 1080p. This implies it has 1,920 pixels throughout, and 1,080 pixels vertically. An Extremely HD 4K TV has twice that quantity, each vertically and horizontally, and 8K has twice that.
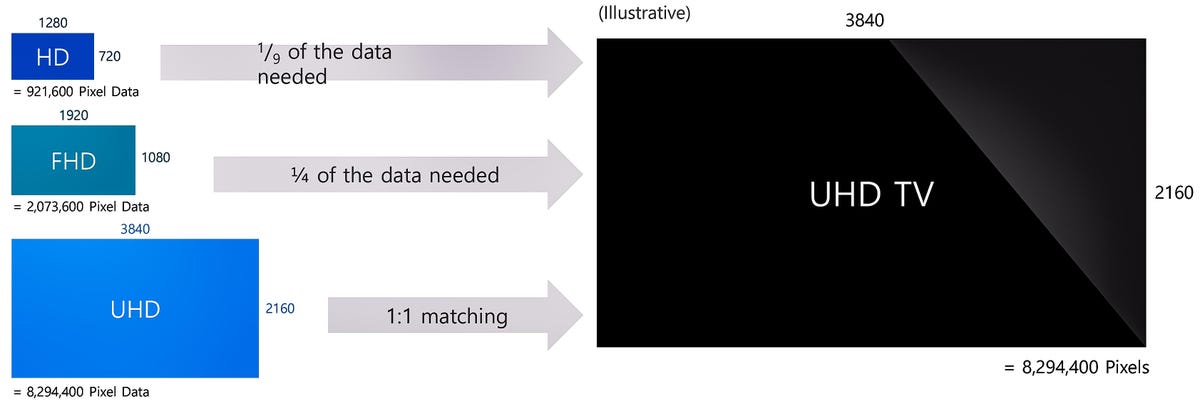
As you possibly can see, non-4K sources, like just about all broadcast and cable tv, have far fewer pixels than 4K TVs. Within the case of 720p sources, like Fox and ABC, there’s solely one-ninth the variety of the pixels wanted to fill a 4K TV. If these had been proven on a 4K TV with out scaling or upconverting, it could simply be a tiny picture within the middle of the display, surrounded by huge black bars.
To create a picture that fills the display, a TV has to have information for each a type of pixels. If you happen to ship a 1080p TV the video from a 1080p Blu-ray, there is no downside. The supply, Blu-ray, has the identical variety of pixels because the TV.
The problem is when not all content material has the identical decision as your TV. If you play a DVD, with its decision of 720×480 in your 1080p TV, the TV has to create all-new pixels to fill the display. The identical is true on
4K TVs
when exhibiting 1080p video. Since 4K TVs have twice the horizontal and vertical decision, they want 4 instances as many pixels to create a picture.
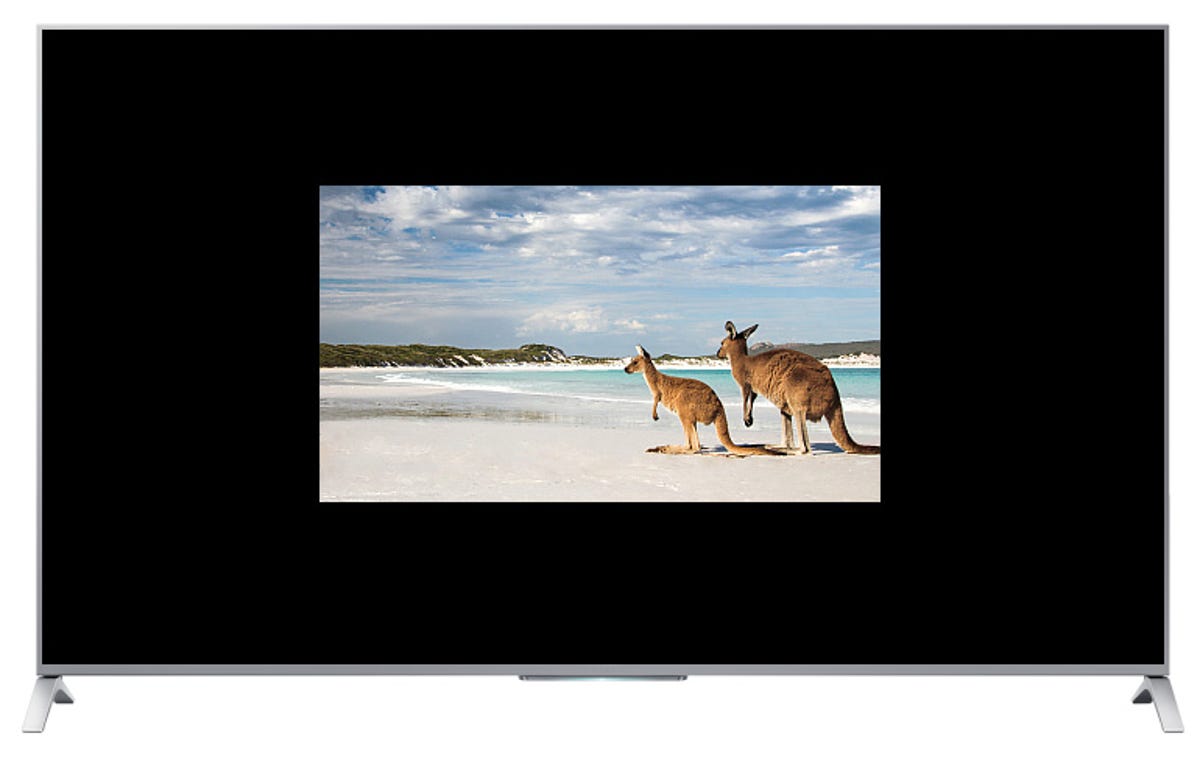

1080p on a 4K TV with out upconversion would have numerous black area.
This course of of making new pixels is named upconversion, upscaling, or simply scaling. All of them imply the identical factor, and it is primarily “zooming in” on a low-resolution picture, so it may possibly fill a bigger, high-resolution display.
There are a lot of methods to do that, however the easiest to grasp is simply creating further, equivalent pixels from every unique. For 1080p to 4K upconversion, you’d want 4 pixels from every unique one.
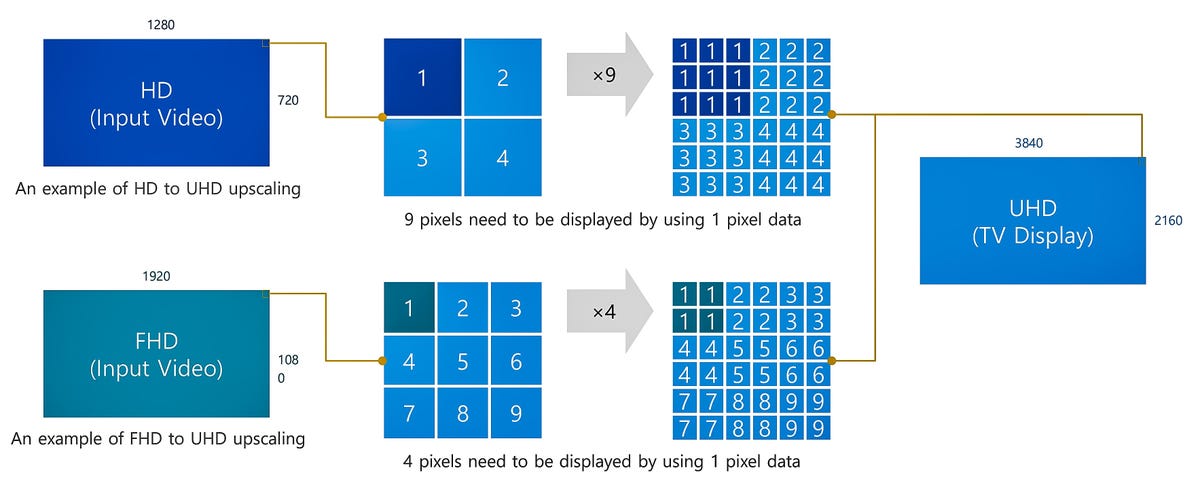
Within the easiest type for scaling, the unique pixels are duplicated to suit the required greater decision. So the brand new 4K sign has 4 pixels, for instance, to the HD unique’s one. Extra superior variations of scaling do extra to find out what the brand new pixels must be.
Scaling know-how superior as
processors
received quicker, and TV corporations regarded for added methods to enhance picture high quality. As a substitute of one thing easy like a one-into-four pixel conversion, processors take a look at the adjoining pixels to find out what the brand new pixels ought to appear like. This allowed for sharper, extra outlined edges. Sharper, extra outlined edges in flip seem to the attention like extra element. Or to place it one other manner, your DVD would not look fairly as mushy as it could have with older or cheaper scaling strategies.
Quick-forward a number of extra years and processors had been wanting not simply at adjoining pixels in every body, however at a number of frames to search for movement, noise and lots of different components to create a picture with as a lot element as attainable, whereas maintaining video noise and different image artifacts at a minimal. That is an oversimplification, however we speak concerning the course of in additional element in Why your 4K TV might be the one 4K converter you want.
It seems that figuring out the correct amount quantity of
sharpness
, noise discount, and different components is a job AI can probably do higher.

CNET’s David Katzmaier reads the wonderful print on an 8K Samsung TV.
Enter synthetic intelligence and machine studying
Usually, engineers designing a TV use their very own secret sauce to get the very best picture out of their firm’s newest video processor. They’d would decide what mixture of sharpness enhancement, noise discount, and so forth would look greatest with the widest number of content material.
Usually no matter they got here up with must be a kind of “one dimension matches all,” in that it must look “good” with all content material. Even when barely completely different settings would possibly look nice with some photos however worse with others. Possibly sports activities would look higher with extra edge restoration, however films would look unnatural. Or films would look higher with extra noise discount, however reside TV would look mushy. These particular settings are referred to as filters.
Although it could be attainable to have a handful of various filters in a TV, discovering the precise one requires an excessive amount of fiddling from customers. Are you able to think about having a choice of 10 completely different filters and needing to determine if Sport no. 7 or Sport no. 8 is best for the blistering motion of the most recent snooker championship? Nobody would try this.
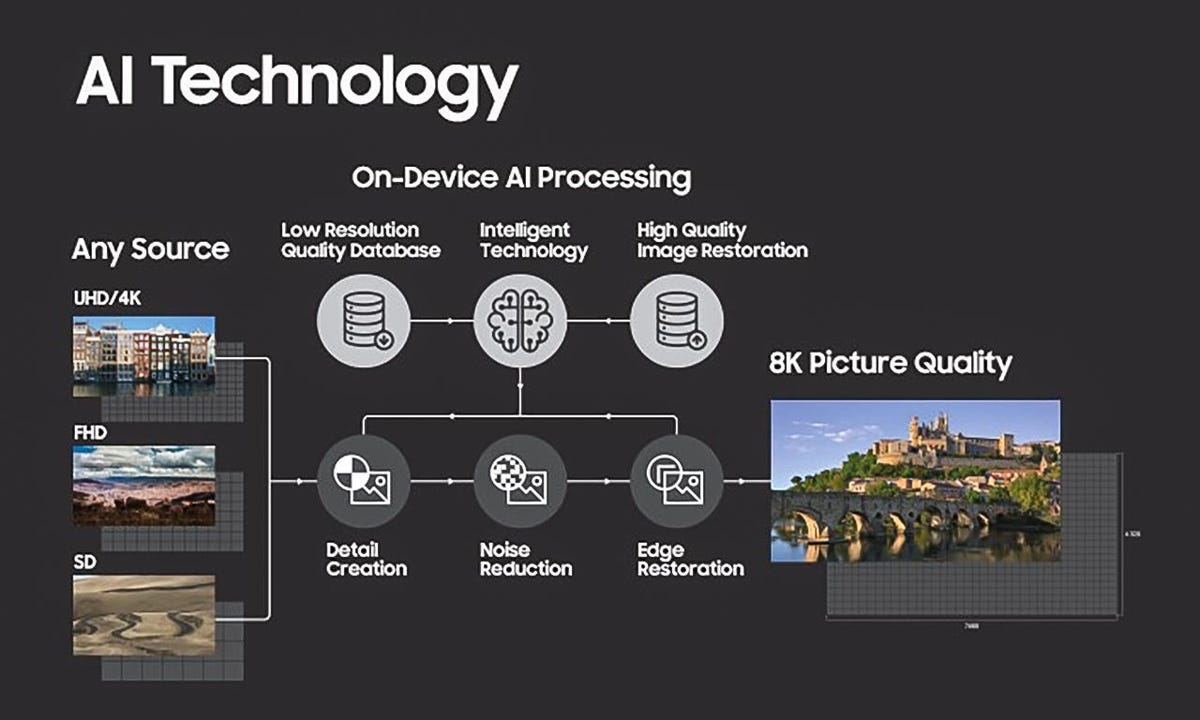
The varied steps in Samsung’s AI Upscaling course of.
Enter AI. There are two points to Samsung’s AI upscaling. The primary is machine studying. Video content material — heaps and plenty of video content material — will get analyzed by computer systems. From this, new filters are created. There may be a filter for soccer, one for auto racing, one for actuality TV, one for motion films, one for dramas and so forth. There’s even, doubtless, completely different filters for 1080p sports activities versus 4K sports activities. Samsung claims they’ll have “over 100” completely different filters.
These filters can be saved in every TV. That brings us to half 2. If you’re watching one thing, the TV will analyze the picture and decide what you are watching. It would then apply the filter it determines will look the very best, mechanically. If these engineers (and their laptop colleagues) work out a even higher filter, they’ll even ship that to the TV through a software program replace.
In idea, a particular filter will create a better-looking picture than a generic filter. How a lot better? Effectively, in all probability not an enormous quantity. It might be inconceivable to say precisely, however between high-end TVs of the identical model, the one with the AI upscaling would possibly look somewhat higher on sure content material. That comparability is inconceivable to make, although, as a result of it is doubtless a wholly completely different processor within the two TVs.
LG, Sony, and others
Samsung is actually not alone, although they appear to be the primary to mix these strategies on this particular manner. LG and Sony, for instance, every have their very own strategies which are comparable.
LG’s AI ThinQ is an umbrella title for a number of “AI” applied sciences that embody voice recognition and voice-controlled assistants, which is not what we’re speaking about right here. LG additionally makes use of AI to reinforce the picture high quality, albeit in a barely completely different manner than Samsung. In line with LG, a “deep studying algorithm” checked out over 1 million items of content material. This lets the TV analyze what you are watching and choose the very best total settings for that exact content material. They’re calling this Deep Studying Image.
That is, it appears, a kind of hybrid of the previous technique and Samsung’s AI technique, in that it makes use of AI to find out the very best of what the engineers have carried out within the TV. Nonetheless LG’s model may also embody points like bearing in mind the ambient mild (“AI Brightness”) within the room, just like what most
smartphones
do. Although not precisely what we’re discussing right here, the TV may also analyze and alter the audio relying on the content material. So primarily it is all a bit like extra superior, smarter “Auto” image and sound modes.
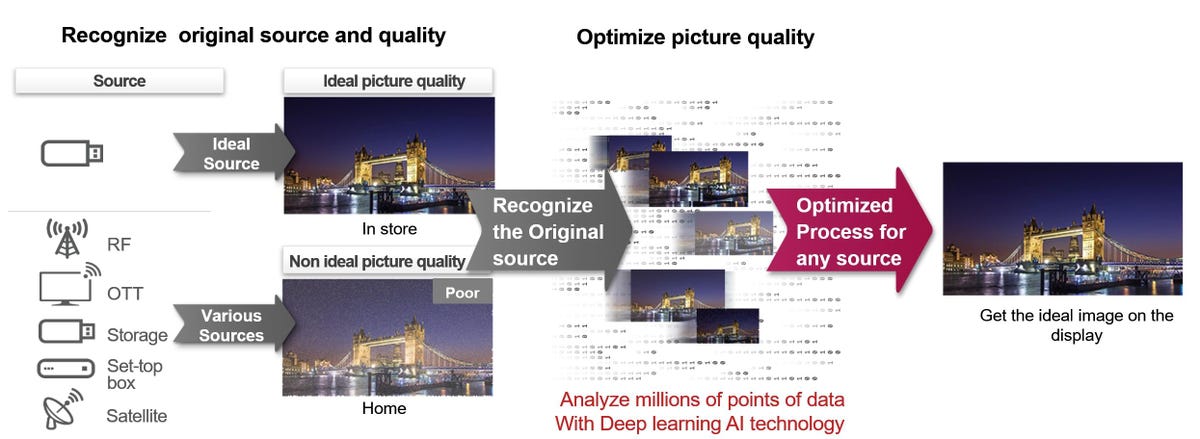
Sony would not name its processing “AI” something, however its 4K X-Actuality Professional works equally to Samsung’s AI upscaling, drawing on an in depth picture database to tell its picture correction. Sony’s time period is “twin database processing.” One database is used to find out what elements of a picture want noise discount, and one other database is used to find out what elements want element enhancement.

The video picture is analyzed and in comparison with, as Sony claims, an “evolving” database of photos, to find out how greatest to use noise discount and element enhancement.
As picture processing turns into higher, quicker, and cheaper, count on to see extra of this “sensible” picture processing from different corporations. There is not any manner any TV producer can know the whole lot everybody will present on their TV, however they’ll design a processor that is sensible sufficient to find out what it’s you are watching, and ensure the TV appears to be like its greatest exhibiting it. That in itself is not new, however how nicely TVs do it continues to get higher.
Scaling to the longer term
Video scaling has come a great distance, however it’s no substitute for the true factor. Whereas we look forward to extra precise 4K and 8K video, nonetheless, it is price noting how a lot “simpler” it’s for the TV whenever you begin with high quality content material.
HD-to-8K conversion requires an identical degree of pixel creation as did DVD-to-HD conversion. However should you begin with HD content material, and add the skills of contemporary processing, an 8K TVs will doubtless look higher with non-8K content material than early HDTVs did with non-HD content material.
Going ahead, count on extra corporations to undertake some model or variation of AI upscaling. It is one other small step within the infinite marathon to enhance picture high quality. Just a little scaling enchancment right here, a touch of excessive dynamic vary there, and abruptly TVs look a lot better than they did even a number of years in the past. That is progress.
In addition to overlaying TV and different show tech, Geoff does picture excursions of cool museums and places around the globe, together with nuclear submarines, huge plane carriers, medieval castles, airplane graveyards and extra.
You’ll be able to comply with his exploits on Instagram and YouTube, and on his journey weblog, BaldNomad. He additionally wrote a bestselling sci-fi novel about city-size submarines, together with a sequel.






