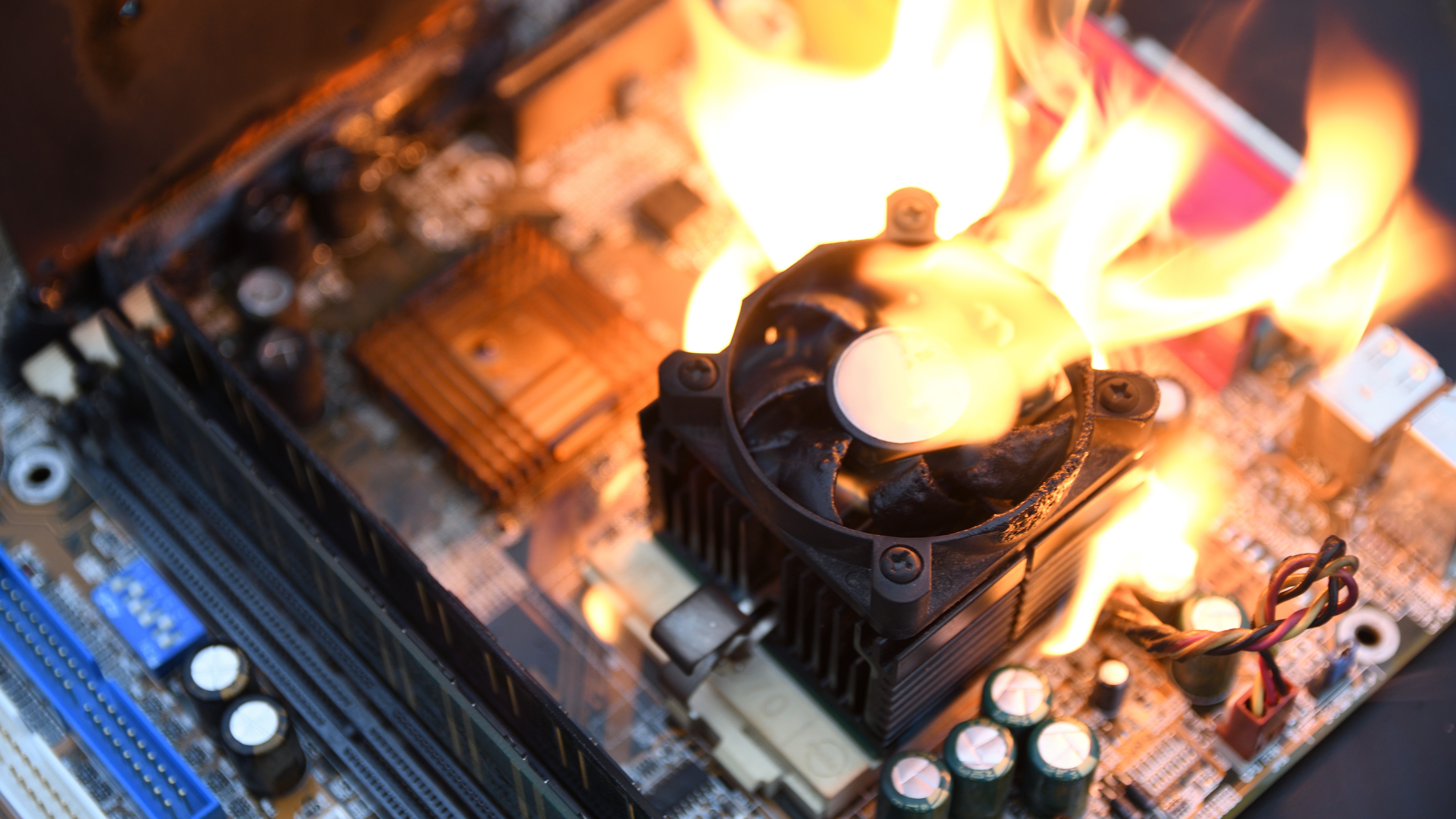
On April 25 I reported that some AMD Ryzen 7000 CPUs have been immediately burning out, inflicting harm to the processors themselves, and in some circumstances to the related motherboard.
Fortunately, AMD has rapidly gotten to the foundation of the problem, and issued a well timed AGESA firmware replace for the 600-series AM5 motherboards that help the next-gen CPUs, which can restrict the voltage to the chip to 1.3V. AMD stated in a press release that it expects board companions to launch BIOS updates containing the brand new firmware inside the subsequent few days.
As I beforehand reported, it was suspected that unsafe overvolting was the reason for the thermal points, as voltages in extra of 1.35V gave the impression to be damaging the chips’ thermal security measures and permitting them to succeed in unsafe temperatures.
Now, should you don’t overclock any of your parts, you possibly can simply go forward and shut this text, since that type of overvolting was solely occurring when customers have been manually overclocking their CPU (or utilizing sure in-BIOS overclocking profiles). The difficulty was affecting each Ryzen 7000 and 7000X3D chips, most notably the flagship Ryzen 9 7950X3D.
Penalties for overclocking?
Should you’re nonetheless studying, you’re little question conscious that overclocking one’s parts is a standard follow amongst PC players and tech lovers. That is achieved both by utilizing a pre-loaded profile within the motherboard BIOS, or by manually elevating the goal working frequencies and provided voltage to your PC elements. We’ve received a information on learn how to overclock proper right here, should you’ve saved studying out of curiosity!
This new firmware could come as a blow to overclocking followers, because it appears to be like like loads of Ryzen 7000 chips can the truth is be safely overclocked above 1.3V; I famous in my earlier article that 1.35V gave the impression to be ‘secure’, and judging by the low variety of circumstances reported, we are able to assume that some Ryzen 7000 merchandise can deal with greater than that with the fitting CPU cooling resolution.
On the intense facet, AMD has assured customers in a press release that “none of those modifications have an effect on the power of our Ryzen 7000 Collection processors to overclock reminiscence”, which was a priority some customers had when the problems first arose, and the prospect of a voltage cap repair was advised. There may even be no affect on AMD’s Precision Increase characteristic, which is a type of automated ‘good overclocking’ mode.
Nonetheless, critical overclocking lovers will little question be displeased; the aggressive overclocking scene depends on esoteric liquid nitrogen cooling to push CPUs to extremely excessive frequencies and voltages as a way to eke out treasured further efficiency, and a tough voltage cap on all Ryzen 7000 processors is principally going to close all that down.
It’s additionally unclear at this level whether or not AMD intends to refund any broken chips; in its assertion, it stated that “anybody whose CPU could have been impacted by this concern ought to contact AMD buyer help”, however it ought to be famous that this will solely be for data-gathering functions, since harm attributable to guide {hardware} overclocking is explicitly not lined in Ryzen product warranties.






