Mirrors to the soul: In only a few years, modern generative AI programs have come a great distance in creating realistic-looking people. Eyes and arms are its most important hindrances. Nonetheless, fashions like Steady Diffusion are getting proficient at producing people that, if not excellent, are a minimum of simple to edit, which has sparked issues about misuse.
Researchers on the College of Hull have just lately revealed a groundbreaking methodology to establish AI-generated deepfake photos by analyzing reflections in human eyes. Final week, the staff unveiled the approach on the Royal Astronomical Society’s Nationwide Astronomy Assembly. The strategy employs instruments utilized by astronomers to review galaxies to look at the consistency of sunshine reflections in eyeballs.
Adejumoke Owolabi, an MS pupil on the College of Hull, led the analysis staff supervised by Astrophysics Professor Dr. Kevin Pimbblet.
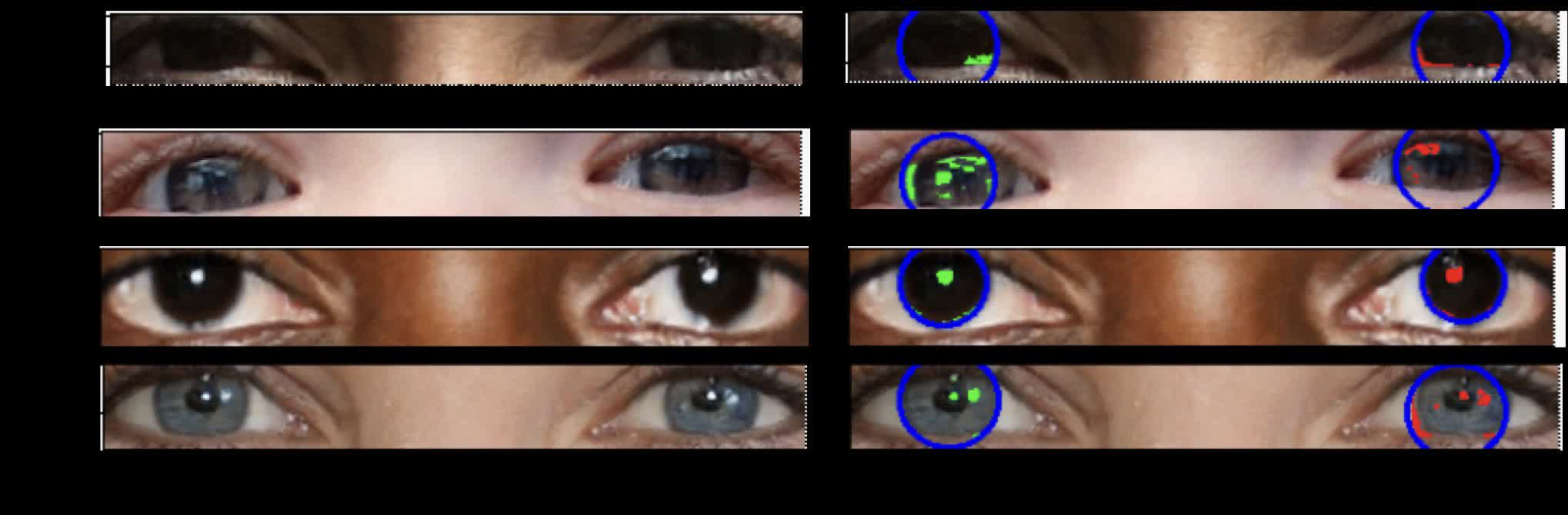
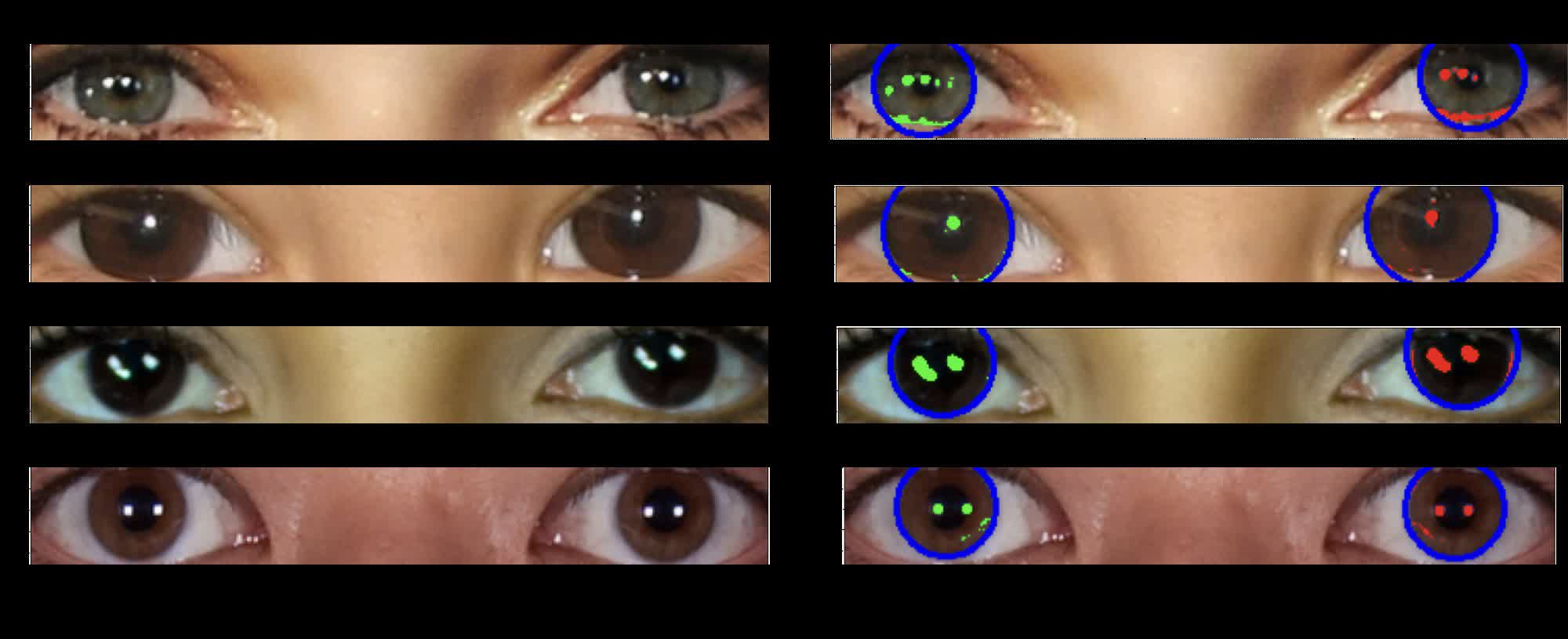
The detection approach works on the precept {that a} pair of eyeballs will mirror mild sources equally. The position and form of sunshine reflections is constant in each eyes in real photos. In contrast, many AI-generated photos do not account for this, resulting in misplaced and oddly formed reflections between the eyes.
The astronomy-based method to deepfake detection might sound extreme since even an off-the-cuff photograph evaluation can reveal inconsistencies in eye reflections. Nevertheless, utilizing astronomy instruments to automate the measurement and quantification of the reflections is a novel development that may verify suspicions, doubtlessly offering dependable authorized proof of fraud.
Pimbblet defined that Owolabi’s approach routinely detects eyeball reflections and runs their morphological options by indices to check the similarity between the left and proper eyeballs. Their findings confirmed that deepfakes typically exhibit variations between the pair of eyes.
The researchers pulled ideas from astronomy to quantify and examine eyeball reflections. For instance, they’ll assess the uniformity of reflections throughout eye pixels utilizing the Gini coefficient, usually used to measure mild distribution in galaxy photos. A Gini worth nearer to 0 signifies evenly distributed mild, whereas a price nearing 1 suggests concentrated mild in a single pixel.
“To measure the shapes of galaxies, we analyze whether or not they’re centrally compact, whether or not they’re symmetric, and the way easy they’re. We analyze the sunshine distribution,” Pimbblet defined.
The staff additionally explored utilizing CAS parameters (focus, asymmetry, smoothness), one other astronomy software for measuring galactic mild distribution. Nevertheless, this methodology was much less efficient in figuring out faux eyes.
Whereas the eye-reflection approach reveals promise, it will not be foolproof if AI fashions evolve to include bodily correct eye reflections. It appears inevitable that GenAI creators will appropriate these imperfections in time. The strategy additionally requires a transparent, up-close view of eyeballs to be efficient.
“There are false positives and false negatives; it is not going to get every thing,” Pimbblet cautioned. “However this methodology supplies us with a foundation, a plan of assault, within the arms race to detect deepfakes.”
Picture credit score: Adejumoke Owolabi